Why Additive Manufacturing
Why is the ADDere Laser-Wire Additive System the Future of Manufacturing?
ADDere’s best-in-class laser-wire additive manufacturing process revolutionizes the manufacturing industry by drastically improving the time to market, reducing the cost of materials, providing consistent performance and eliminating scrap waste.
Time to Market: Casting vs. Additive Manufacturing
A dramatic reduction in time, from the design phase to the completion of the part, is possible with ADDere’s Additive Manufacturing products and services. Parts and processes that could take anywhere from months to even years to create now have the capacity to be accomplished within days or even hours.
Design-to-part usually involves multiple steps that rely on each other’s completion. This process includes several aspects: design approval/lock design, ordering, designing and building fixtures, casts or forms, sourcing of material, casting or forging parts and machining. With conventional processes currently available in the market, delivery times of up to one year are a common time frame for these steps and components.
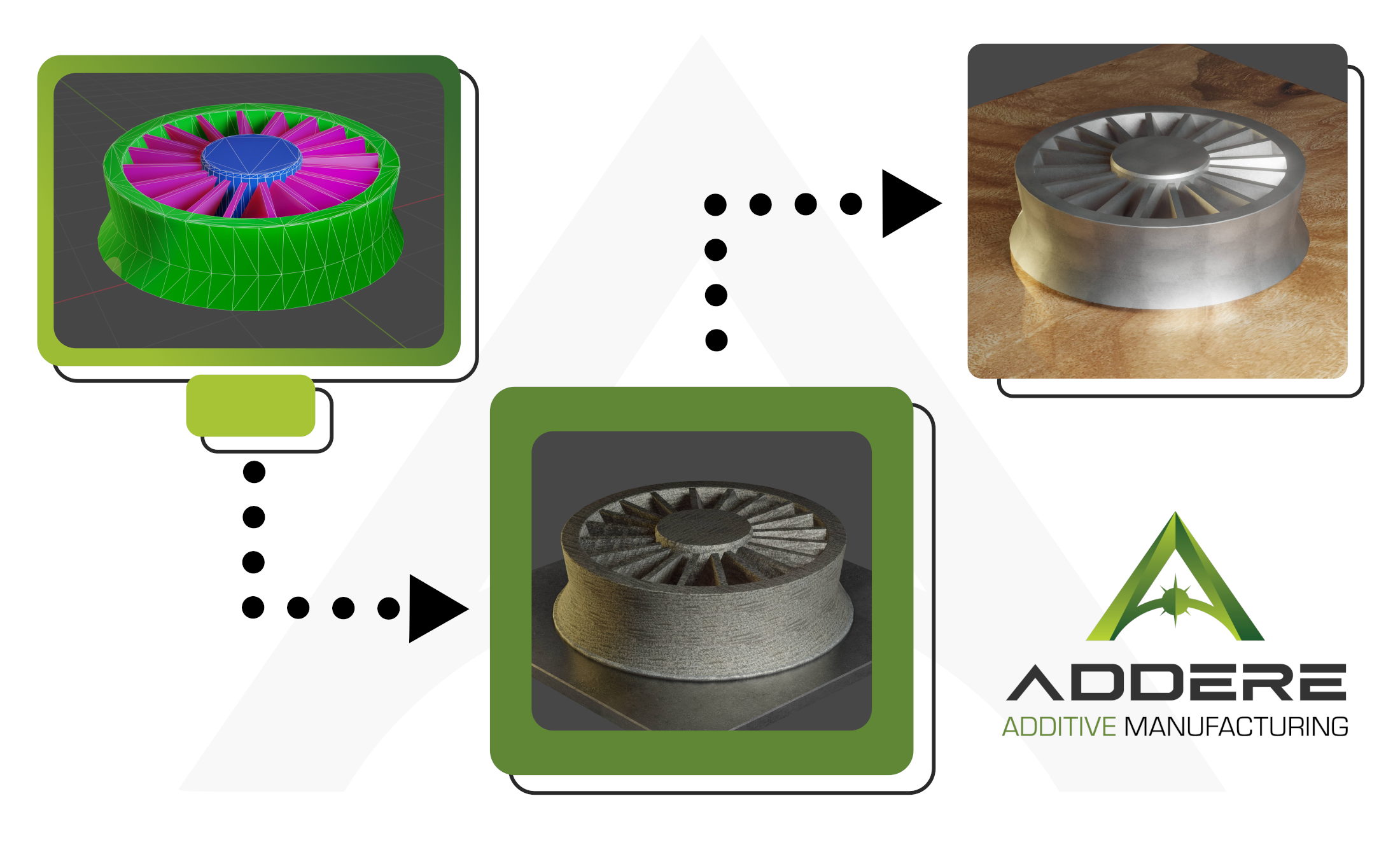
With the ADDere Additive Manufacturing process, time-intensive iterative steps like the component design or fixture building can be greatly reduced. Designs can be sent directly to additive manufacturing systems for processing. This process allows for a much faster design cycle as components and fixtures can be tested at scale and in the materials specified for end use. With ADDere’s systems that could mean even Titanium, Inconel or other exotic metals.
ADDere also offers time advantages over conventional manufacturing processes. Complex parts that would have required casting could be 3D printed in a variety of metals, side-stepping the many steps involved in common casting processes. The laser wire additive system has benefits over milling, especially when considering high-complexity products where 3D printing opens the possibility for geometries that would be difficult to impossible with current milling technologies.
With the ADDere Additive Manufacturing systems, laser-wire metal deposition rates can range from 7 to 22 lbs per hour. These rates will change depending on the metal type and the geometry of the part being built.
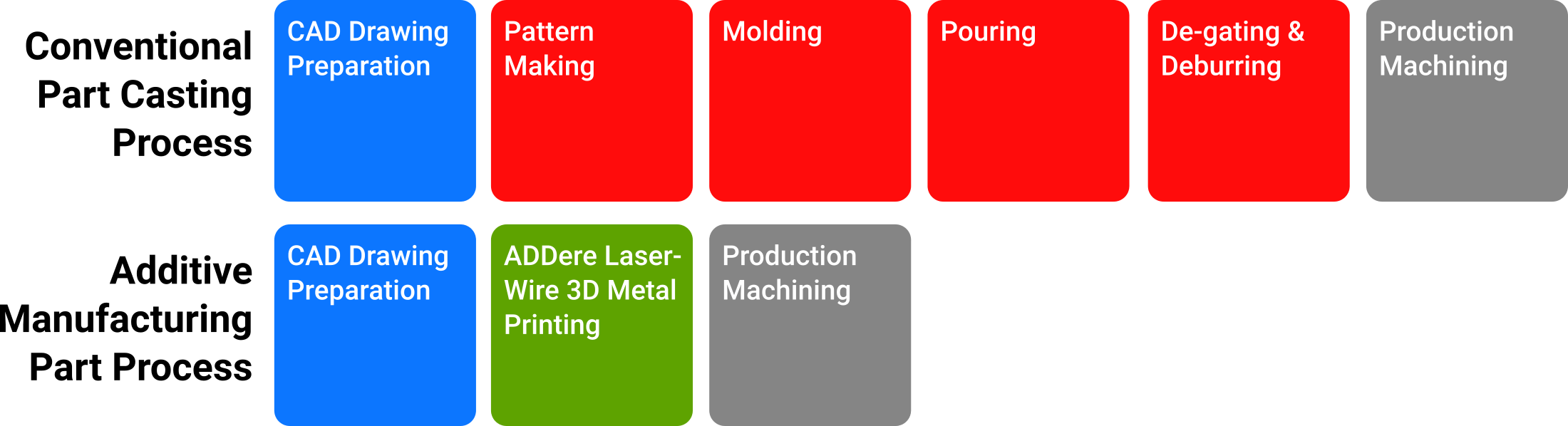
Cost of Materials: Powder vs. Wire Based Deposition
Using reliable laser-wire metal deposition, the additive manufacturing process has the ability to save large amounts of material cost. Close to 100% of the material used in ADDere’s additive metal 3D printing process goes into the component being printed, whereas in a powder-based process material waste is substantially more and the material is prone to impurities.
Typically the cost for the same quantity of material in powder is typically double that of the cost for wire. For more exotic and more expensive materials, this can have a great impact on the total cost of the component. For example, titanium wire costs around 40% of the cost of powder per kilogram.
Performance: Powder vs. Wire Based Deposition
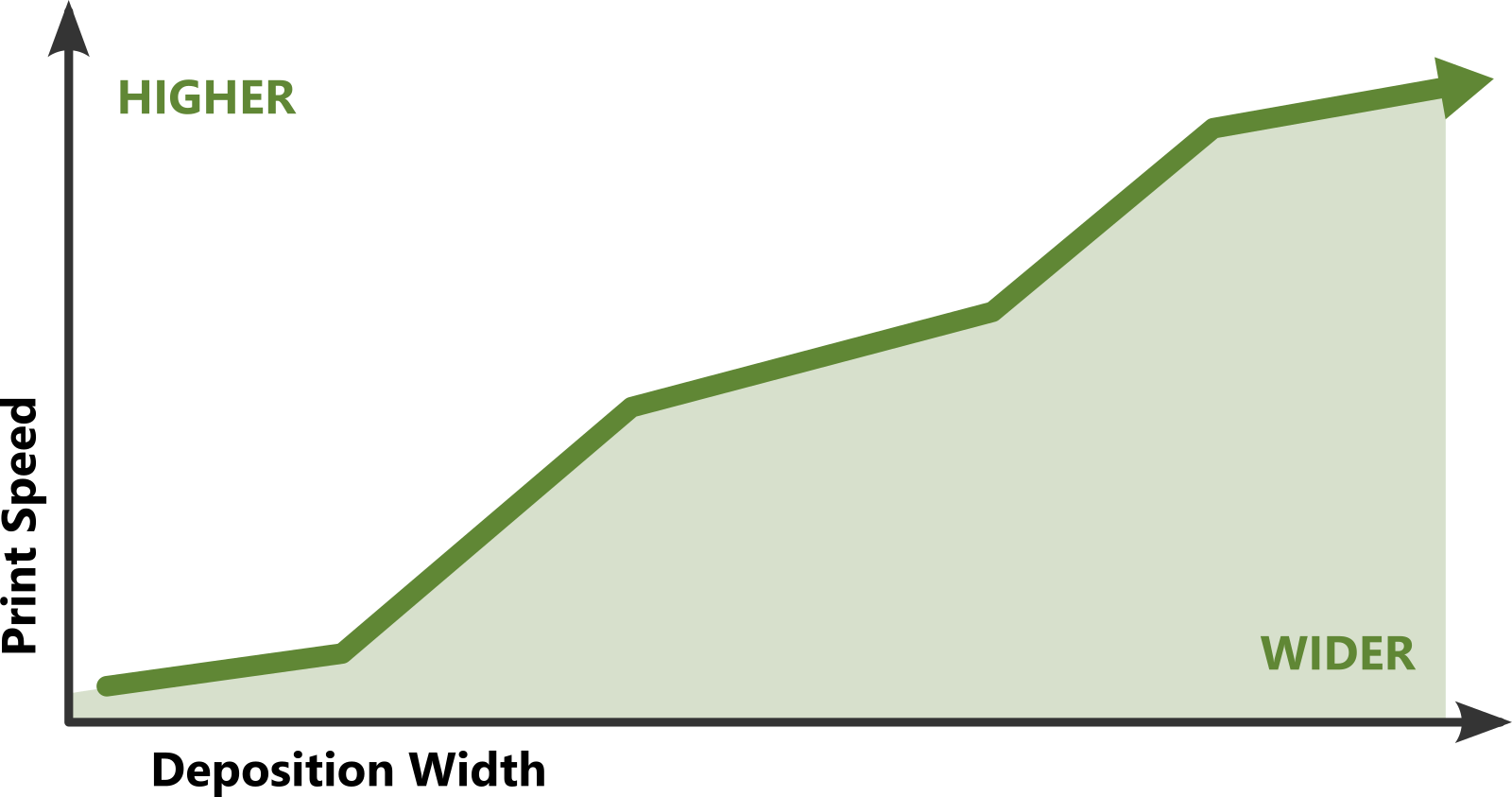
While powder-based deposition works well when producing small intricate parts, powder-based doesn’t provide the speed and metallurgical purity that wire-based would provide. Moreover, powder is an inherently less safe material to work with, being more flammable and more prone to moisture and other impuraties. When printing large-scale parts, wire-based deposition runs at much higher print speeds than powder.
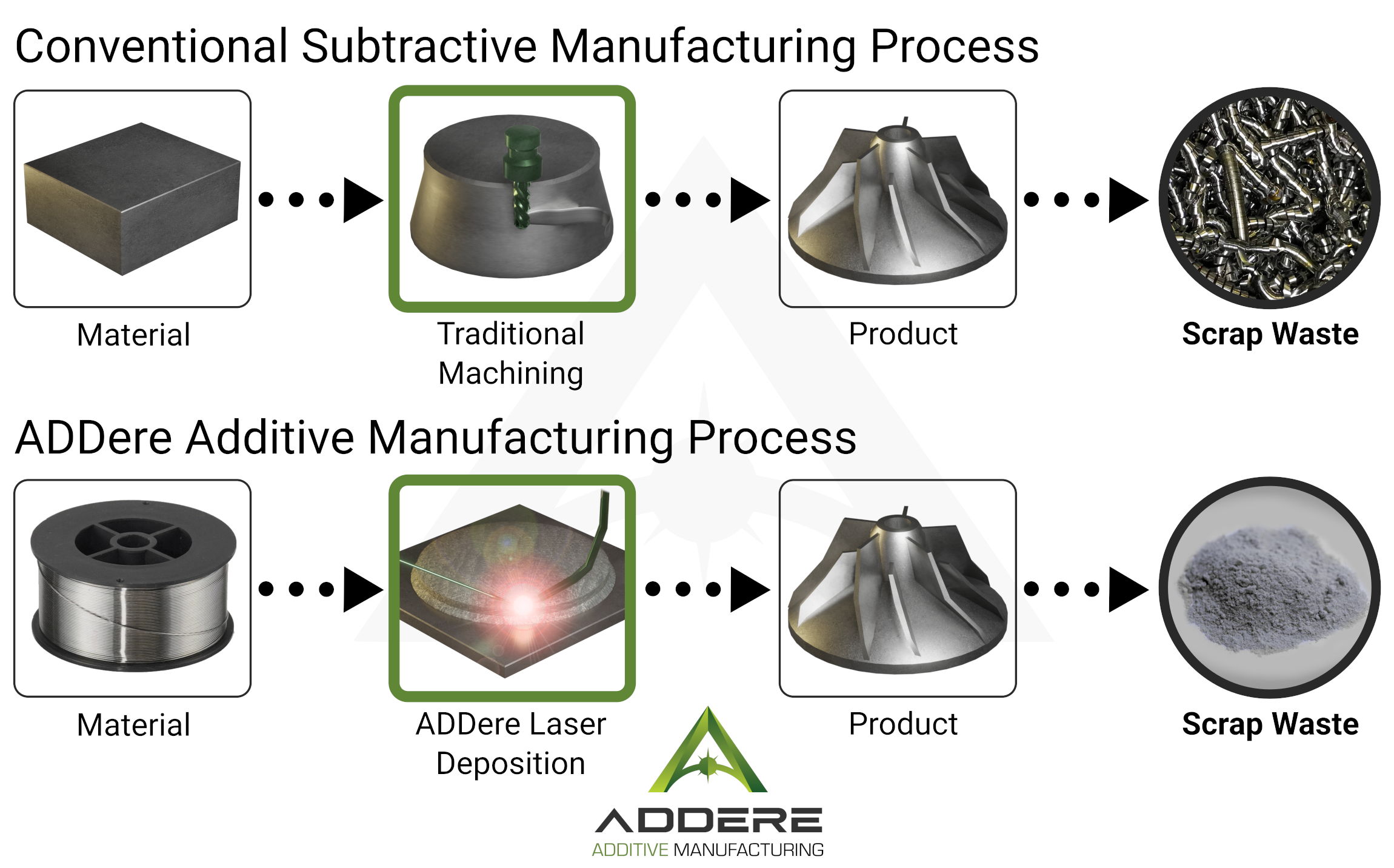
Less Scrap Waste: Subtractive vs. Additive Manufacturing
Conventional subtractive manufacturing processes from a single block of metal require removing a substantial amount of material to build the part leading to a large amount of scrap waste. Whereas additive manufacturing creates parts that are near net shape and require a minimal amount of machining to make the part production ready.
Can ADDere Help Your Business?
If ADDere’s high-quality large-scale metal additive manufacturing process sounds like something that your firm would benefit from, whether it’s in aerospace, defense, oil & gas or any other industry, contact us today. The ADDere laser-wire additive manufacturing process can produce large-scale builds in a wide range of sizes and materials near net shape to fit all your manufacturing needs.
do you want to learn more about ADDere's products and services?
What's going on at ADDere
Latest Blog Posts

Where the ADDere Additive Process Excels Over Metal Casting
Metal casting and additive manufacturing are the two most common methods of producing large-scale metal parts. Metal casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold
Trends and Future Prospects in Large-Scale Metal 3D Printing
Industrial Metal additive manufacturing is not a new technology or concept. Still, it has gained significant momentum in recent years in many industries, thanks to
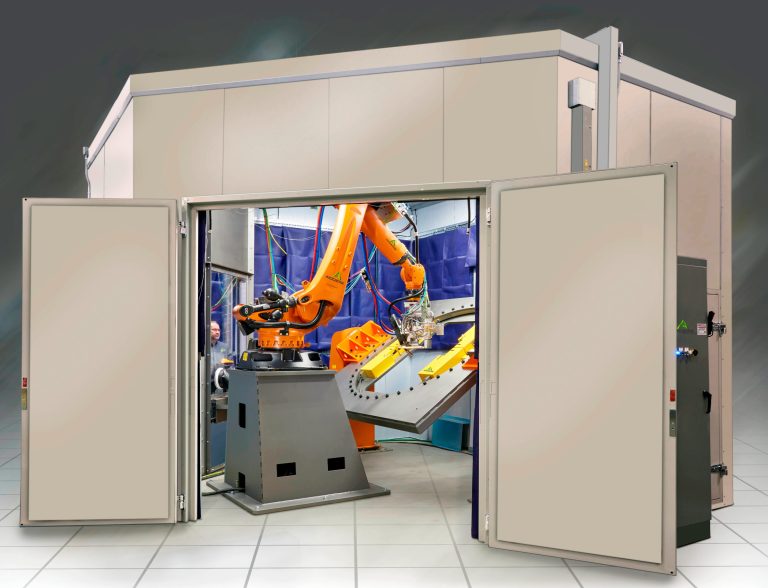

The Opportunities of Additive Manufacturing for Sustainable Development & Circular Economy
ADDere’s additive manufacturing process contributes to sustainable development and a circular economy by reducing material waste, energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions and transportation costs. It
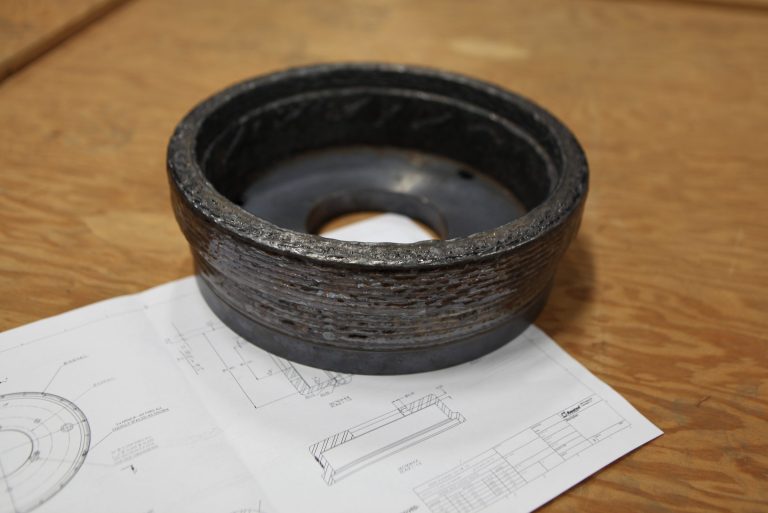

How Additive Manufacturing Can Reduce Production Lead Times
Production lead time is a critical variable for companies that rely on production and manufacturing processes to produce goods. In traditional manufacturing processes, it can
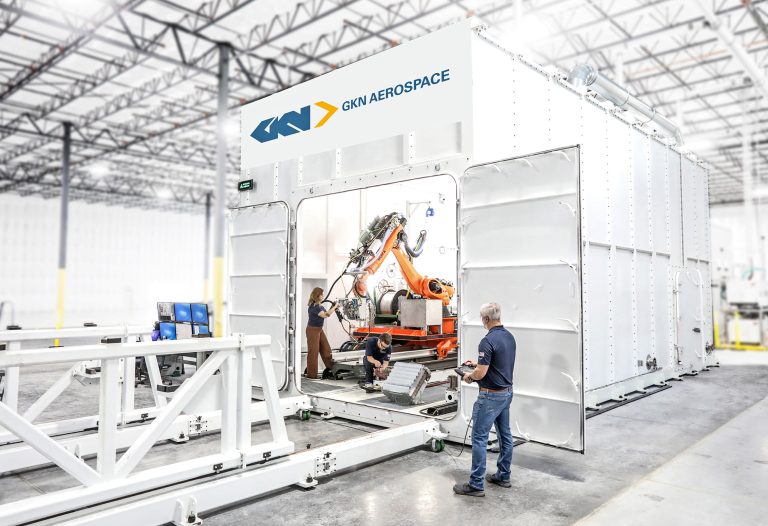

ADDere Provides GKN Aerospace with the Industry’s Largest Additive Manufacturing System
Building large-scale titanium parts for aerospace applications requires the largest metal 3D printer available. Because of the demanding nature of aerospace components and their previous
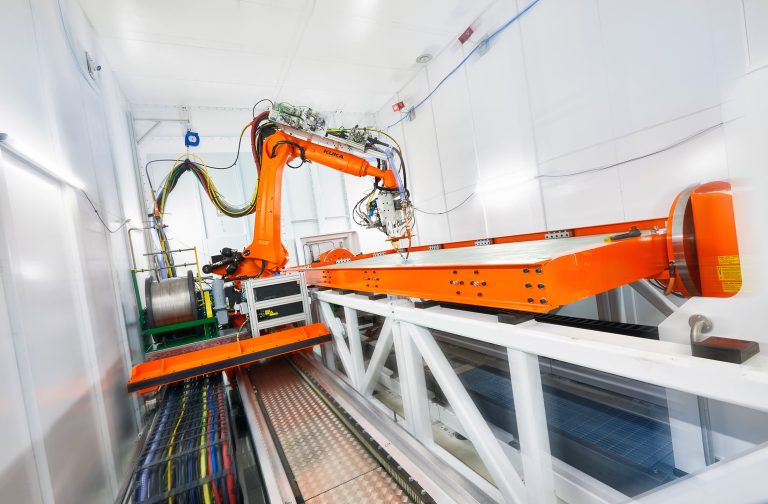

Unlocking Synergies: How Hybrid Manufacturing Can Enhance Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is a revolutionary technology that enables the creation of complex geometries and customized parts. However, metal additive parts have some limitations, such as


